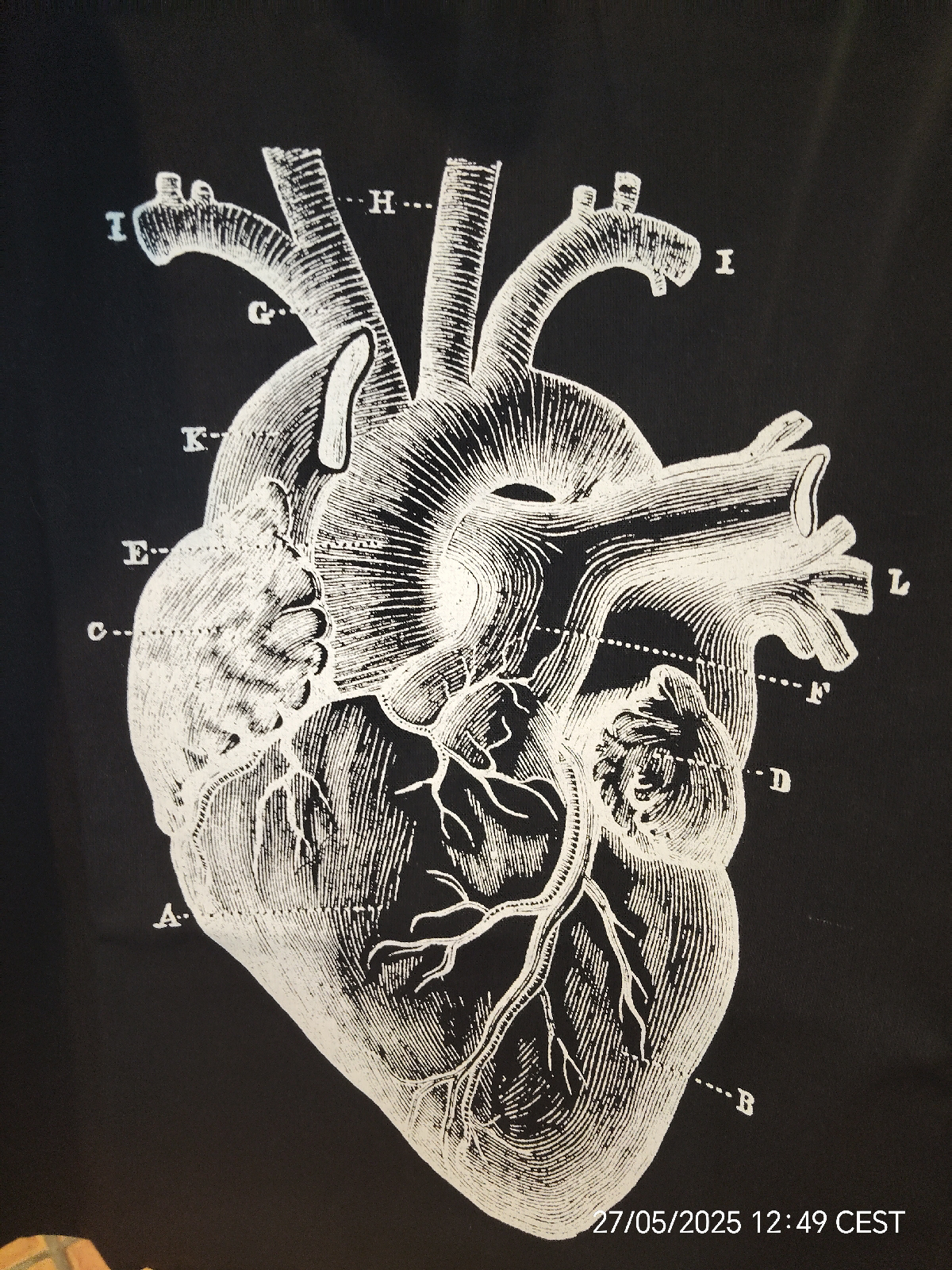
Ewing and all cell related health issues
(For those who battle with Faith, Love, and Unity)
Explorador de futuro ,...
I always say/write the same set of information.
For all related cell health issues....@bioecirganic proposals as prophylactic or preventive, but part of
#BioTerapy, significant actions
I will include in this project https://easyhealthycellsproject.blogspot.com/2023/06/biotherapy-ehcp-elguezabal-et-al-before.html
the Bamboo Patch for feet Bamboo Patch for feet
also the organic colostrumorganic colostrum
and these vitamin mineral supplements
Mikel E & ChatGPT
.
Q:
Ewing sarcoma starter at the genetic level. Heavy metal Pollution as the main enhancer of this bone capsules cancer
R:
Ewing sarcoma is a rare and aggressive type of bone cancer that primarily affects children and adolescents. At the genetic level, Ewing sarcoma is characterized by specific chromosomal translocations, most commonly t(11;22)(q24;q12), which results in the fusion of the EWSR1 gene on chromosome 22 with the FLI1 gene on chromosome 11. This translocation creates a fusion protein that acts as an aberrant transcription factor, driving oncogenesis by dysregulating gene expression.
### Genetic Basis of Ewing Sarcoma
1. **EWSR1-FLI1 Fusion Protein**:
- The EWSR1-FLI1 fusion protein is present in approximately 85% of Ewing sarcoma cases.
- This chimeric protein has potent oncogenic properties, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, and altered cell differentiation.
2. **Secondary Genetic Alterations**:
- In addition to the primary fusion gene, secondary genetic alterations, such as mutations in TP53, STAG2, and CDKN2A, may contribute to tumor progression and poor prognosis.
### Role of Heavy Metals in Ewing Sarcoma
Heavy metals are environmental pollutants that can have various toxic effects on human health. There is growing evidence suggesting that exposure to heavy metals might enhance the risk or progression of certain cancers, including Ewing sarcoma, through several mechanisms:
1. **Genotoxicity**:
- Heavy metals such as cadmium, arsenic, and chromium can induce DNA damage directly by generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) or by interfering with DNA repair mechanisms.
- This genotoxic stress can lead to mutations or chromosomal aberrations, potentially promoting oncogenic transformations.
2. **Epigenetic Modifications**:
- Heavy metals can also cause epigenetic changes, such as DNA methylation, histone modification, and microRNA expression alterations.
- These epigenetic modifications can disrupt normal gene expression patterns, potentially enhancing the expression of oncogenes or silencing tumor suppressor genes.
3. **Immune System Suppression**:
- Chronic exposure to heavy metals can suppress the immune system, reducing its ability to detect and eliminate cancerous cells.
- An impaired immune response can allow for the unchecked growth and spread of malignant cells.
4. **Oxidative Stress**:
- The accumulation of ROS due to heavy metal exposure can cause oxidative damage to cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- Persistent oxidative stress can create a tumor-promoting environment by activating various signaling pathways related to cell survival, proliferation, and metastasis.
### Potential Mechanisms Linking Heavy Metals and Ewing Sarcoma
1. **Enhancement of Fusion Gene Expression**:
- Some studies suggest that environmental toxins, including heavy metals, may influence the expression levels of fusion genes like EWSR1-FLI1, potentially enhancing their oncogenic effects.
2. **Promotion of Inflammatory Responses**:
- Heavy metals can induce chronic inflammation, creating a microenvironment that is conducive to tumor growth and progression.
3. **Interference with Treatment Efficacy**:
- Exposure to heavy metals may also interfere with the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents used to treat Ewing sarcoma, complicating management and prognosis.
### Conclusion
Understanding the genetic basis of Ewing sarcoma is crucial for developing targeted therapies. While the role of heavy metals as enhancers of Ewing sarcoma remains an area of active research, current evidence suggests they may contribute to cancer development and progression through multiple mechanisms, including genotoxicity, epigenetic changes, immune suppression, and oxidative stress. Further studies are needed to clarify these links and to develop effective strategies for prevention and treatment in populations exposed to heavy metal pollution.

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario